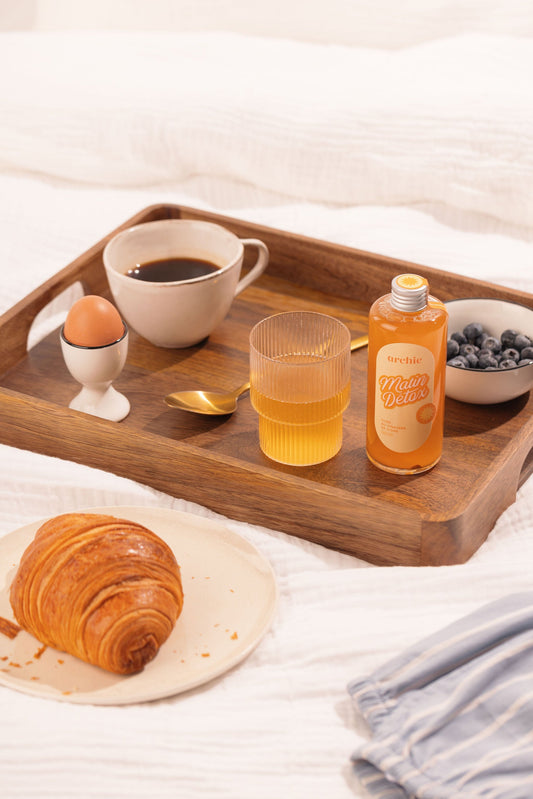
Diabetes is a chronic disease that requires careful management, especially when it comes to diet. A balanced diet is essential for controlling blood sugar levels, preventing long-term complications, and plays a vital role in preventing new diabetes-related complications from developing. This article explores the principles of a diabetes-friendly diet, which foods to eat and avoid, and tips for planning healthy meals and snacks.
Understanding Diabetes and the Importance of Proper Nutrition
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease characterized by abnormally high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. This is due to either insufficient insulin production (type 1 diabetes) or insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production (type 2 diabetes). Type 1 diabetes, in particular, is considered an autoimmune disease, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows glucose to enter cells for energy.
There is also a form of diabetes called gestational diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and can lead to complications for both mother and child if not managed properly. Regardless of the type of diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is essential to prevent long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney problems, and blindness.
The Links Between Diet and Diabetes Management
Diet plays a role in diabetes management. A well-balanced diet can help control blood sugar, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of complications. Food choices directly influence blood glucose levels, making meal planning especially important for people with diabetes.
Eating habits can have a significant impact on diabetes management. The foods we eat, how often we eat, and portion sizes can all affect our blood sugar levels. By eating a balanced diet and following specific dietary guidelines, people with diabetes can better control their blood sugar levels and live healthier, more active lives.
Basic Principles of a Balanced Diet for Diabetics
Carbohydrates: friend or foe?
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy, but they have a direct impact on blood sugar levels. It’s important to choose complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits. These carbohydrates are digested more slowly, which helps prevent blood sugar spikes.
Simple carbohydrates, on the other hand, are quickly absorbed and can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. These carbohydrates are often found in processed foods, sugary drinks, and sweets. For effective diabetes management, it is recommended to limit the consumption of simple carbohydrates and focus on complex carbohydrates.
Carbohydrate counting is a common method used by people with diabetes to manage their carbohydrate intake. It involves calculating the number of grams of carbohydrates in each meal and snack to ensure that you do not exceed a certain daily amount. This method can help maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
The role of fiber in blood sugar control
Fiber is essential for diabetes management because it slows the absorption of sugar and improves blood sugar control. Foods high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Soluble fiber, in particular, can help stabilize blood glucose levels.
Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, promotes digestive health by increasing stool bulk and helping prevent constipation. A diet high in fiber may also aid in weight loss, which is beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes, as weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity.
To increase your fiber intake, try incorporating foods like oatmeal, apples, oranges, carrots, black beans, and chickpeas into your daily diet. It is also important to drink plenty of water when consuming fiber to help it pass through your digestive system.
The Importance of Protein and Good Fats
Protein and healthy fats are also important in a diabetic diet. Protein helps stabilize blood sugar by slowing the absorption of carbohydrates. Sources of protein include lean meat, fish, eggs, low-fat dairy products, and legumes. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, can improve insulin sensitivity.
Protein also plays an important role in building and repairing body tissues, which is essential for maintaining good overall health. For diabetics, it is important to choose protein sources low in saturated fat to avoid contributing to heart problems.
Healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, are particularly beneficial for cardiovascular health. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s. Walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseed oil are also good sources of healthy fats.
The Impact of Apple Cider Vinegar on Blood Sugar
Studies suggest that apple cider vinegar helps reduce blood sugar levels after meals. It is recommended to consume one tablespoon of apple cider vinegar diluted in a large glass of water before meals to benefit from its effects on blood sugar. Apple cider vinegar slows down gastric emptying, which means that carbohydrates are absorbed more slowly, helping to prevent blood sugar spikes.
It is important to note that apple cider vinegar should be consumed with caution, as it is acidic and can damage tooth enamel or irritate the stomach if consumed in large amounts.
As with any supplement or dietary change, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating apple cider vinegar into your diet, especially if you are taking medication for diabetes.
Discover all the benefits of cider vinegar.
Foods to Eat and Avoid for Diabetics
Foods to favor for a diabetic diet
For a diabetic diet, focus on low glycemic foods such as non-starchy vegetables (spinach, broccoli, cabbage), low-sugar fruits (berries, apples), lean proteins (chicken, fish), and whole grains (oats, quinoa).
Non-starchy vegetables are low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great choice for people with diabetes. Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and arugula are especially beneficial because they are high in vitamins and minerals.
Low-sugar fruits, such as berries, apples, and pears, are also good choices because they provide vitamins and fiber without causing blood sugar spikes. It’s important to consume whole fruits rather than fruit juices, as juices often contain added sugars and lack fiber.
Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, tofu and legumes, are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Protein helps with satiety and can prevent between-meal cravings. Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Foods to avoid or eat in moderation
Avoid foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates such as candy, soda, pastries, white bread, and potatoes. Foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods and processed meats, should also be limited.
Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, white rice, and pasta, are digested quickly and can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. It’s best to replace these foods with whole grains, such as whole-wheat bread, brown rice, and whole-wheat pasta, which are digested more slowly and have less of an impact on blood sugar.
Foods high in added sugars, such as candy, baked goods, and sugary drinks, should be avoided because they can cause blood sugar spikes. Sugary soft drinks and fruit juices often contain high amounts of sugar and few nutrients, making them especially harmful for diabetics.
Saturated and trans fats, found in fried foods, processed meats and high-fat dairy products, can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. People with diabetes are already at increased risk of heart problems, so it's important to limit these fats and choose healthier alternatives like unsaturated fats found in olive oil, avocados and nuts.
Manage daily meals and snacks
The importance of breakfast and regular meals
Eating a balanced breakfast helps stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day. Regular, balanced meals that include protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Breakfast is often considered the most important meal of the day, and this is especially true for people with diabetes. A breakfast rich in fiber and protein can help control blood sugar and prevent cravings later in the day. For example, a bowl of oatmeal with berries and chia seeds is a great option for a balanced breakfast.
Eating at regular intervals throughout the day is also important to maintain stable blood sugar levels. It is recommended not to skip meals and not to go more than four to five hours between meals. Healthy snacks can be included between meals to help maintain energy and prevent blood sugar drops.
Balanced Meal Ideas and Healthy Snacks for Diabetics
For breakfast, try a bowl of oatmeal with berries and chia seeds. Oats are a great source of soluble fiber that can help control blood sugar, while berries add vitamins and antioxidants. Chia seeds are high in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids.
For lunch, a quinoa salad with greens, chickpeas, and avocado is a great choice. Quinoa is a whole grain that’s high in protein and fiber, the greens provide essential vitamins and minerals, and the chickpeas add plant-based protein. The avocado provides healthy fats that can improve insulin sensitivity.
For dinner, opt for a grilled salmon fillet with roasted vegetables and brown rice. Salmon is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, roasted vegetables provide fiber and nutrients, and brown rice is a whole grain that has a lower impact on blood sugar than white rice.
For snacks, almonds, carrot sticks with hummus, or an apple with almond butter are great options. Almonds are high in healthy fats and protein, carrot sticks are low in calories and high in fiber, and hummus adds protein and healthy fats. An apple with almond butter combines fiber and healthy fats for a balanced snack.
By following these tips and eating a balanced diet, people with diabetes can better manage their condition and improve their quality of life. It is important to work with a healthcare professional, such as a dietitian or nutritionist, to create a personalized meal plan that meets your specific needs. Effective diabetes management through diet is an integral part of treatment and can not only improve blood sugar levels, but also increase energy, improve mood, and reduce the risk of long-term complications. In all cases, a tailored and individualized approach for each person is essential to optimally manage the disease.